Regulation of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell (HSPC) steady-state egress from the bone marrow (BM) to the circulation is poorly understood. While glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK3β) is known to participate in HSPC proliferation, we revealed an unexpected role in the preferential regulation of CXCL12-induced migration and steady-state egress of murine HSPCs, including long-term repopulating HSCs, over mature leukocytes. HSPC egress, regulated by circadian rhythms of CXCL12 and CXCR4 levels, correlated with dynamic expression of GSK3β in the BM. Nevertheless, GSK3β signaling was CXCL12/CXCR4 independent, suggesting that synchronization of both pathways is required for HSPC motility. Chemotaxis of HSPCs expressing higher levels of GSK3β compared with mature cells was selectively enhanced by stem cell factor-induced activation of GSK3β. Moreover, HSPC motility was regulated by norepinephrine and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1), which increased or reduced, respectively, GSK3β expression in BM HSPCs and their subsequent egress. Mechanistically, GSK3β signaling promoted preferential HSPC migration by regulating actin rearrangement and microtubuli turnover, including CXCL12-induced actin polarization and polymerization. Our study identifies a previously unknown role for GSK3β in physiological HSPC motility, dictating an active, rather than a passive, nature for homeostatic egress from the BM reservoir to the blood circulation.
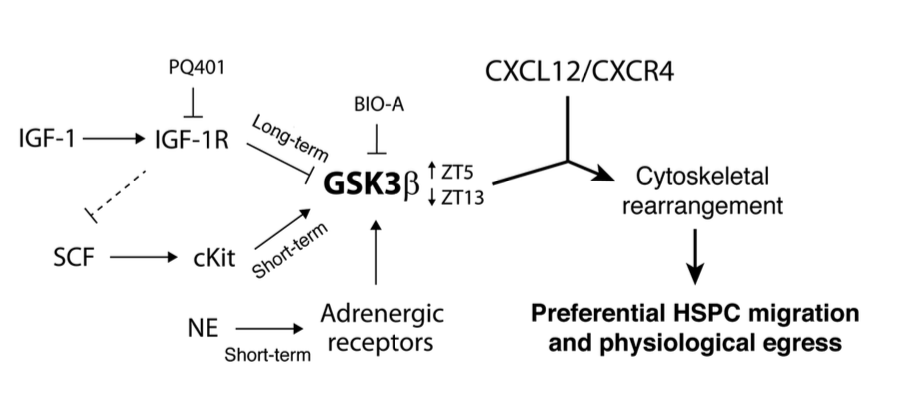
Go to the full article: Kfir Lapid, Tomer Itkin, Gabriele D’Uva, Yossi Ovadya, Aya Ludin, Giulia Caglio, Alexander Kalinkovich, Karin Golan, Ziv Porat, Massimo Zollo, Tsvee Lapidot. GSK3β regulates physiological migration of stem/progenitor cells via cytoskeletal rearrangement. The Journal of clinical investigation, 2013
 We won the poster session at the conference ISCS “The 4th Young Investigators Stem Cell Meeting” organized by the Israeli Stem Cell Society (December 2, 2012. Tel Aviv, Israel).
We won the poster session at the conference ISCS “The 4th Young Investigators Stem Cell Meeting” organized by the Israeli Stem Cell Society (December 2, 2012. Tel Aviv, Israel).
 We developed Bitnos.com, a free, web-based, collaborative Operating System that provides you all the best free online biomedical applications, search engines and websites. With online applications and services (also known as web applications or webware), you do not need to download and install anything. All the services will be directly available for you in one click. These applications and services are cross-platform, running via your browser as a client irrespective of what operating system you are using. You just need to access them online.
We developed Bitnos.com, a free, web-based, collaborative Operating System that provides you all the best free online biomedical applications, search engines and websites. With online applications and services (also known as web applications or webware), you do not need to download and install anything. All the services will be directly available for you in one click. These applications and services are cross-platform, running via your browser as a client irrespective of what operating system you are using. You just need to access them online.